AI SaaS Development Playbook: Ship Faster With RalphBlaster + AI Coding Agents
A practical, screenshot-backed walkthrough for teams building SaaS faster with an agent-driven workflow and review controls.
Most AI SaaS content tells you what tools exist. Very little shows a reproducible workflow that ships production-ready features faster. This article is structured to show exactly how to develop SaaS faster with autonomous AI coding workflows and human quality gates.
Use this page as the final article shell while screenshot assets are being captured. The structure is tuned for ai saas, saas artificial intelligence, and saas agent intent.
The catalyst for this piece was Mac Martine's original RalphBlaster demo on January 16, 2026. Keep this embed in the final version as the \"origin story\" proof point:
What AI SaaS development means in 2026
For operators, AI SaaS development is less about chat prompts and more about a repeatable production workflow. You create a ticket, pick the right planning template, run implementation in an isolated branch, and review output before merge.
This matters for SEO and real delivery outcomes: it reframes ai in saas from a vague concept into a measurable system that small teams can execute every day.
- Structured input: ticket + template choice.
- Autonomous output: isolated branch execution.
- Human control: review gates and regeneration loop.
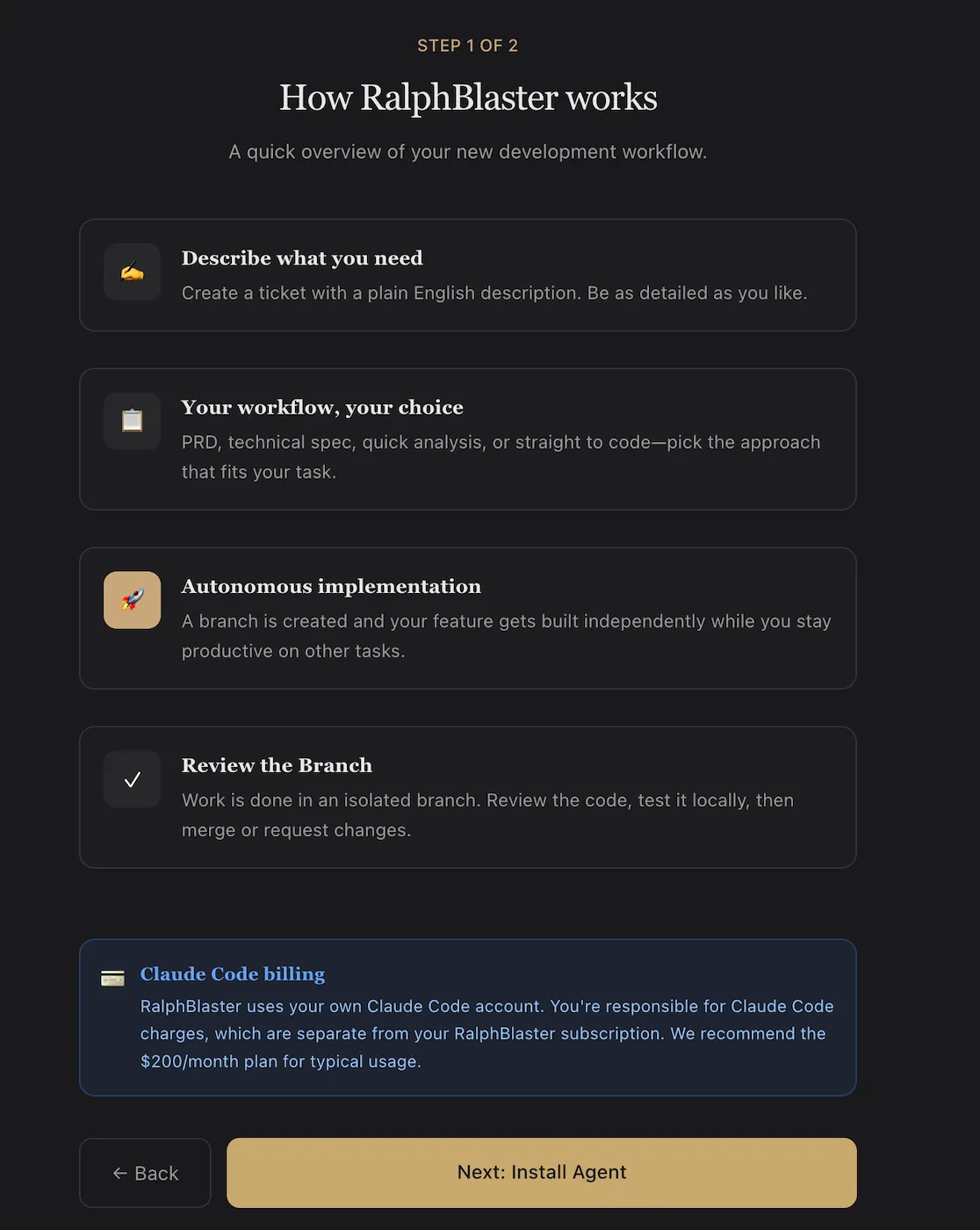
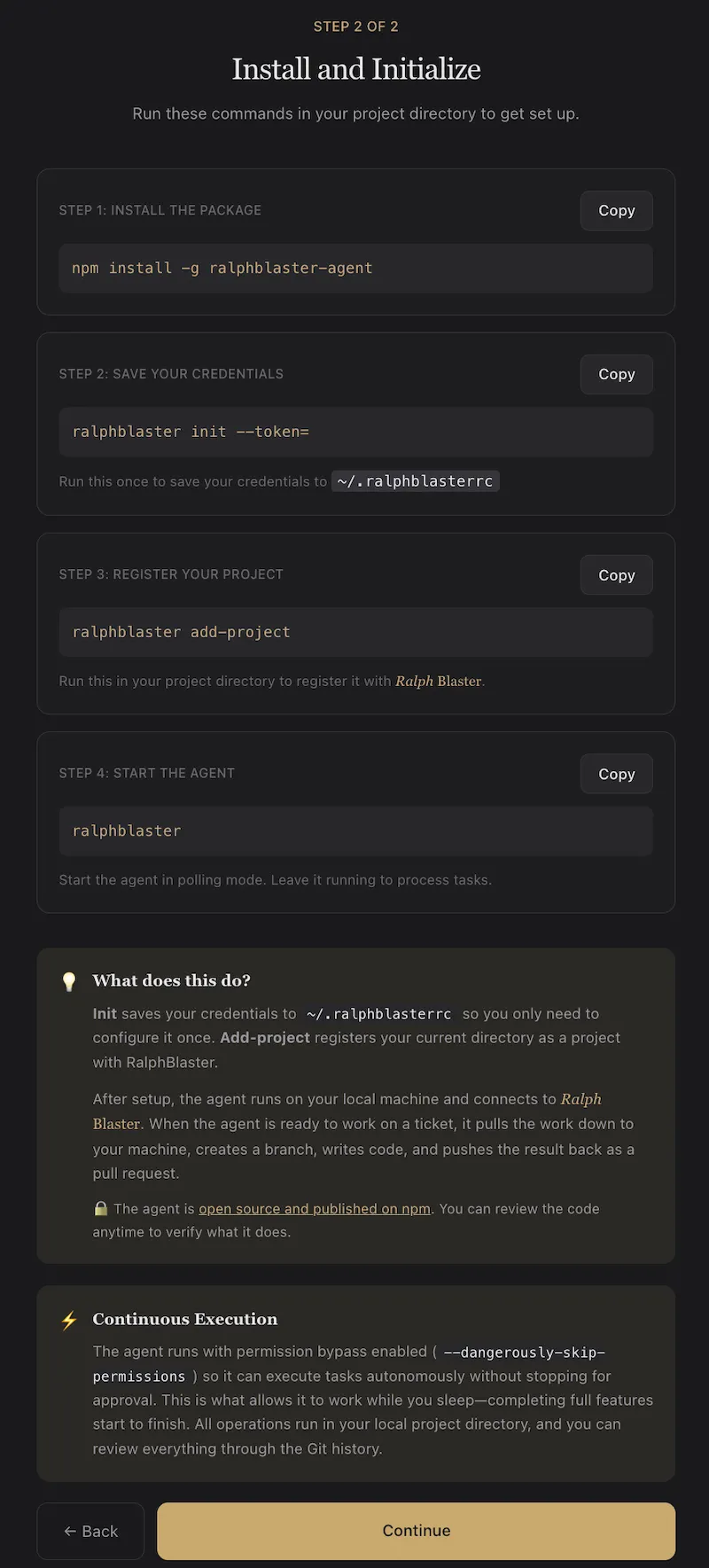
Install and initialize the agent
The install flow shown in-product is explicit and lightweight. You install the local agent once, initialize credentials, register the current project, then run the agent in polling mode.
npm install -g ralphblaster-agent
ralphblaster init --token=YOUR_TOKEN
ralphblaster add-project
ralphblasterOnce registered, the workspace is linked to RalphBlaster and tasks can execute in isolated branches with reviewable output.
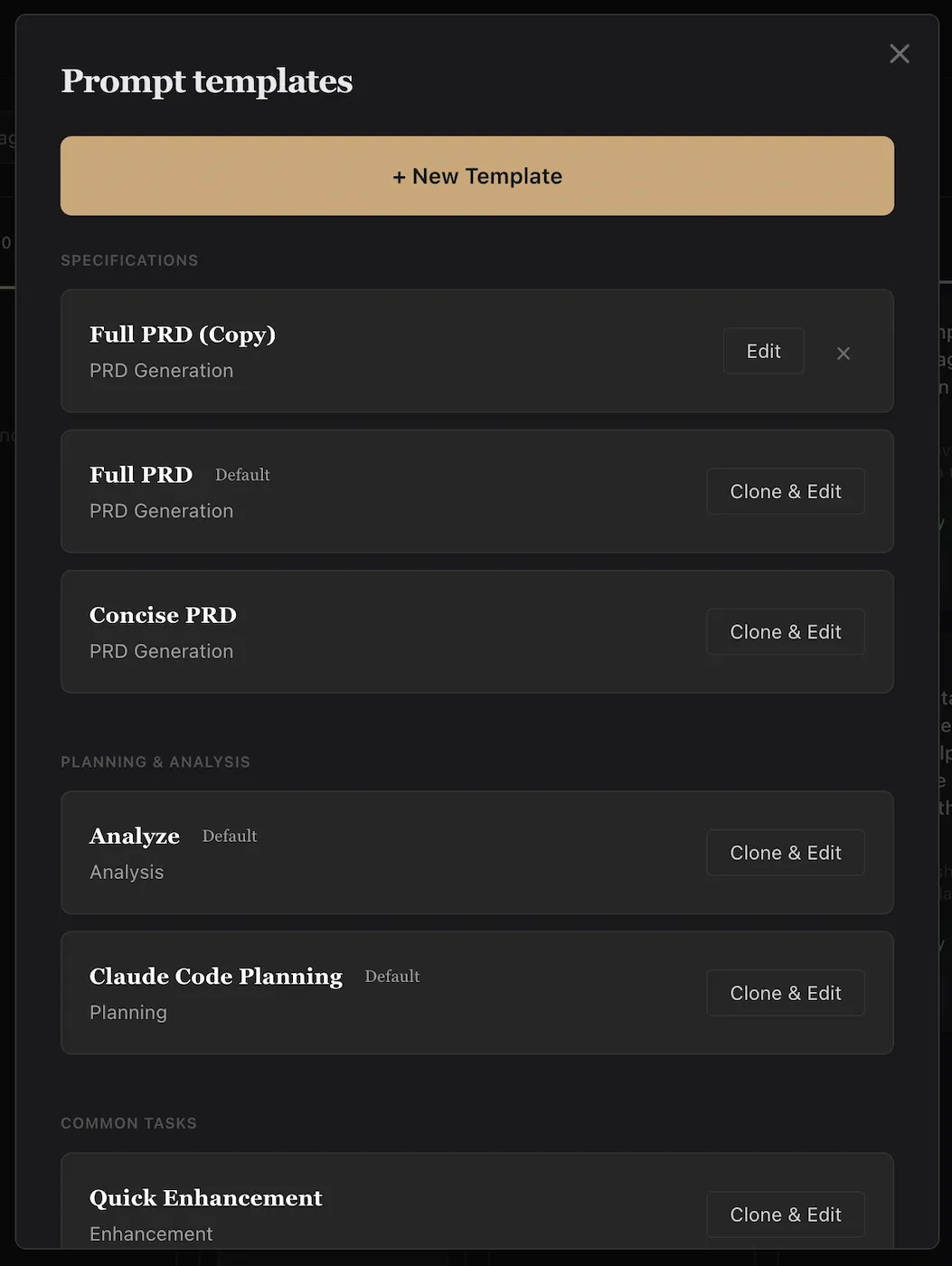
Choose your workflow template per ticket
RalphBlaster's template model is one of the biggest workflow accelerators. Instead of writing new prompt scaffolding every time, teams choose from prebuilt pathways like Full PRD, Concise PRD, Analyze, Claude Code Planning, and Quick Enhancement.
This reduces planning friction and makes delivery behavior consistent across tickets.
Ticket to PRD to isolated branch execution
In this flow, one ticket can produce a full requirements document before implementation. The ticket view shows workflow selection, PRD status, and controls to edit or regenerate requirements.
Natural keyword targets in this section: saas agent, ai agent saas, and saas ai tools.
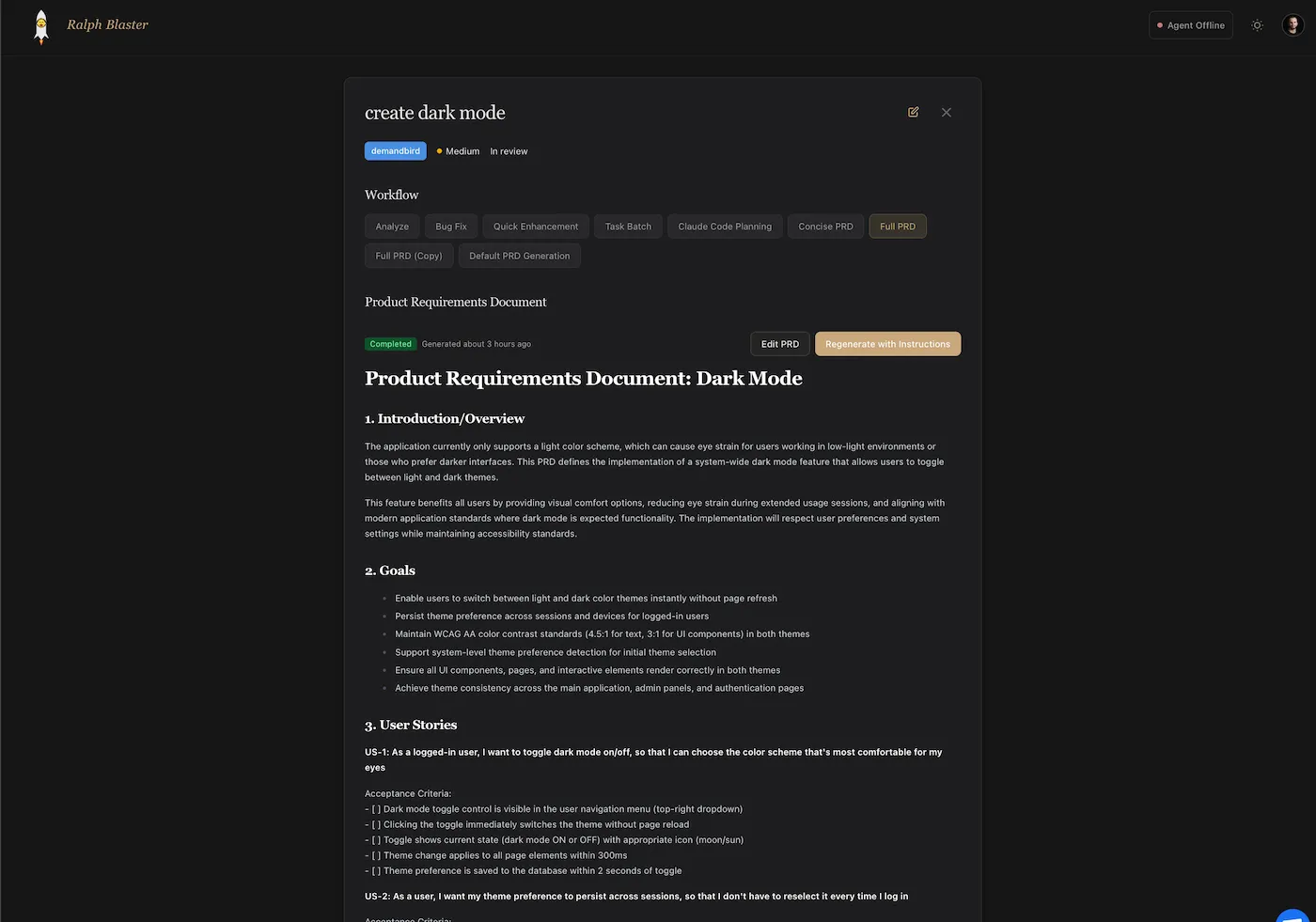
Operate from Kanban, not prompt chaos
The board-level view gives teams shared visibility into the full task lifecycle: Backlog, Up Next, In Review, In Progress, In Testing, and Completed. You can also see PRD-ready and completion markers directly on cards.
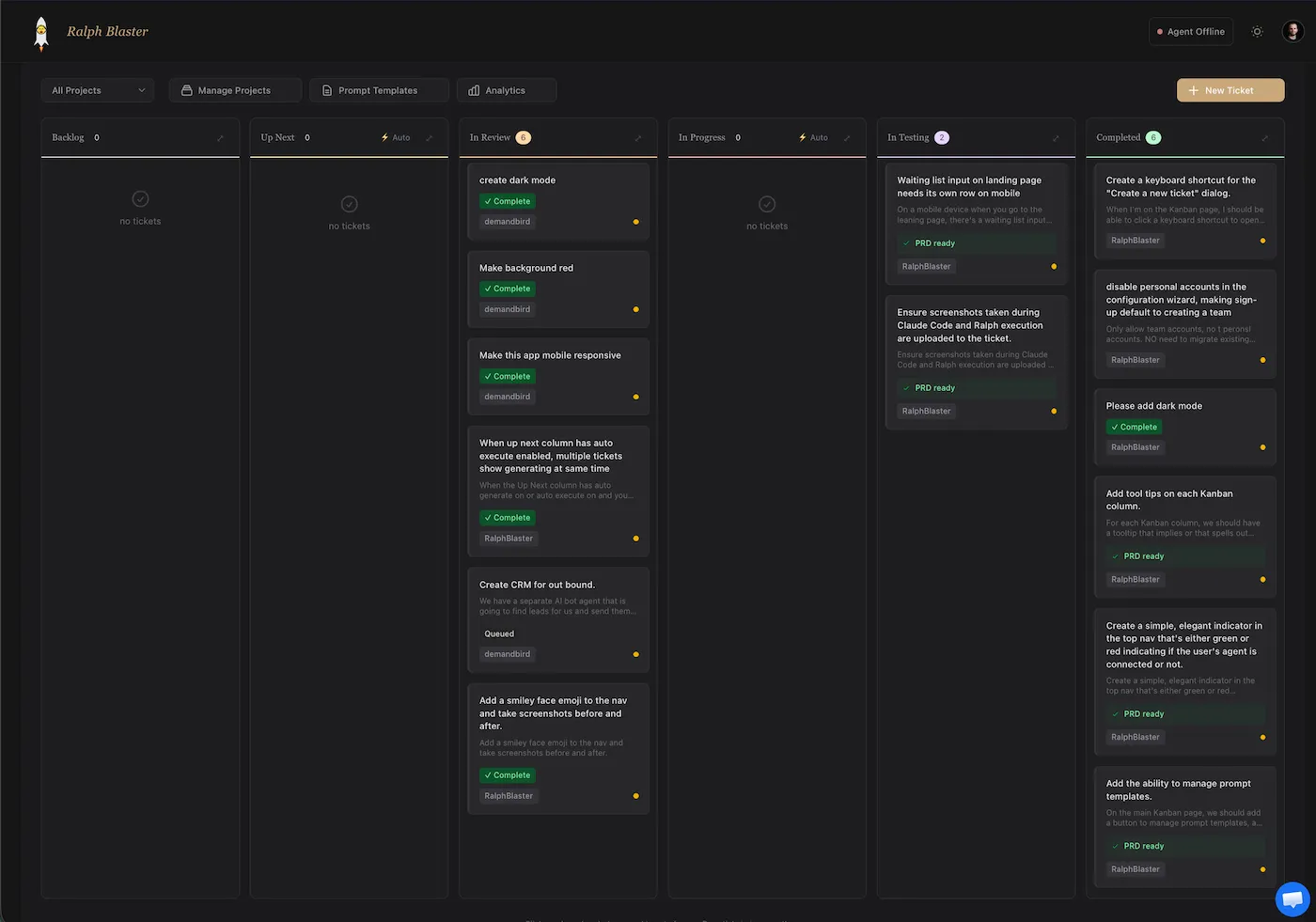
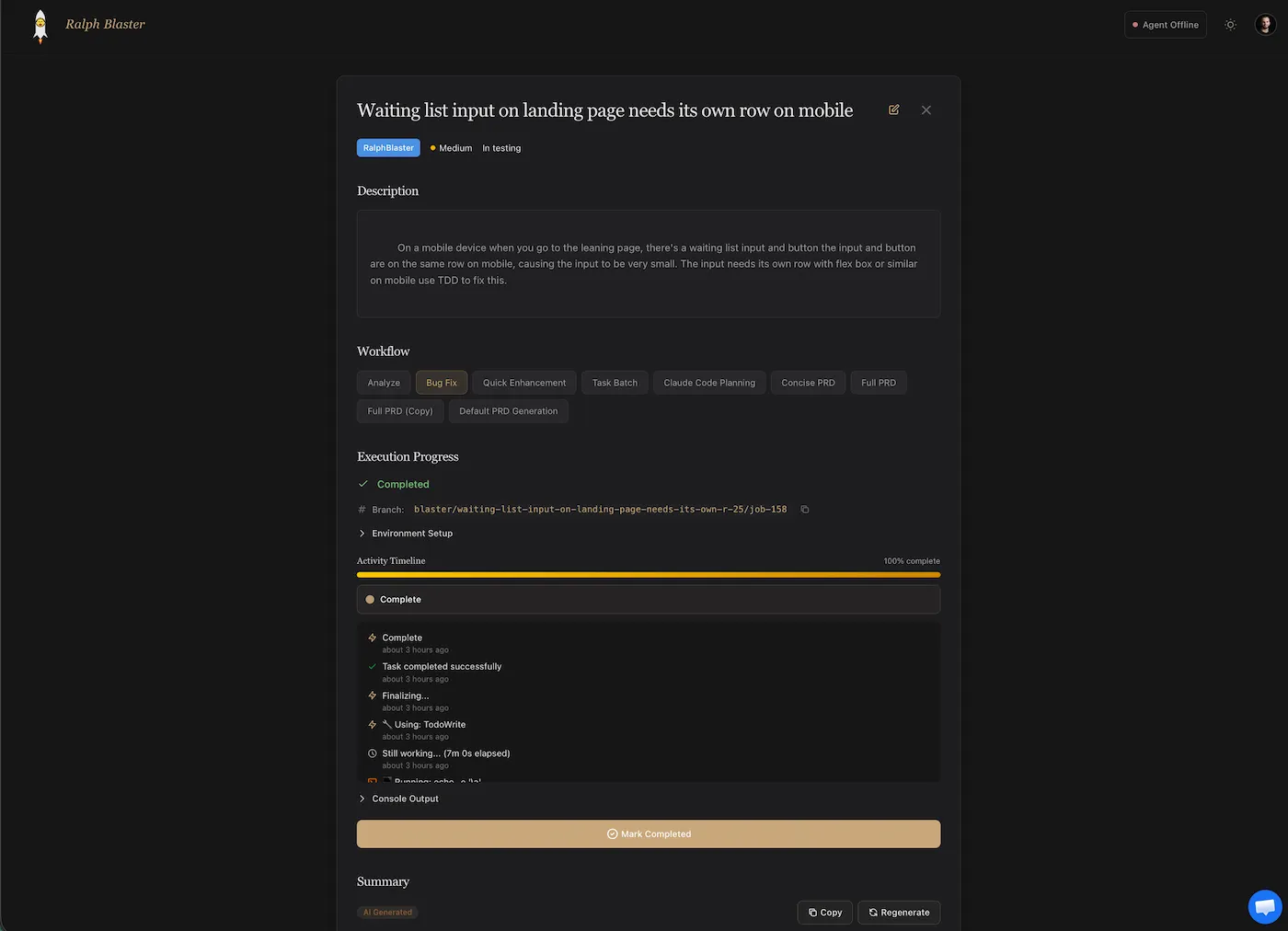
Execution detail view: branch trace, timeline, and regeneration
The ticket detail view shows execution progress, branch identity, environment setup, activity timeline, and console output. This gives you auditability before approving changes.
When output needs refinement, regeneration controls make iteration explicit instead of ad-hoc.
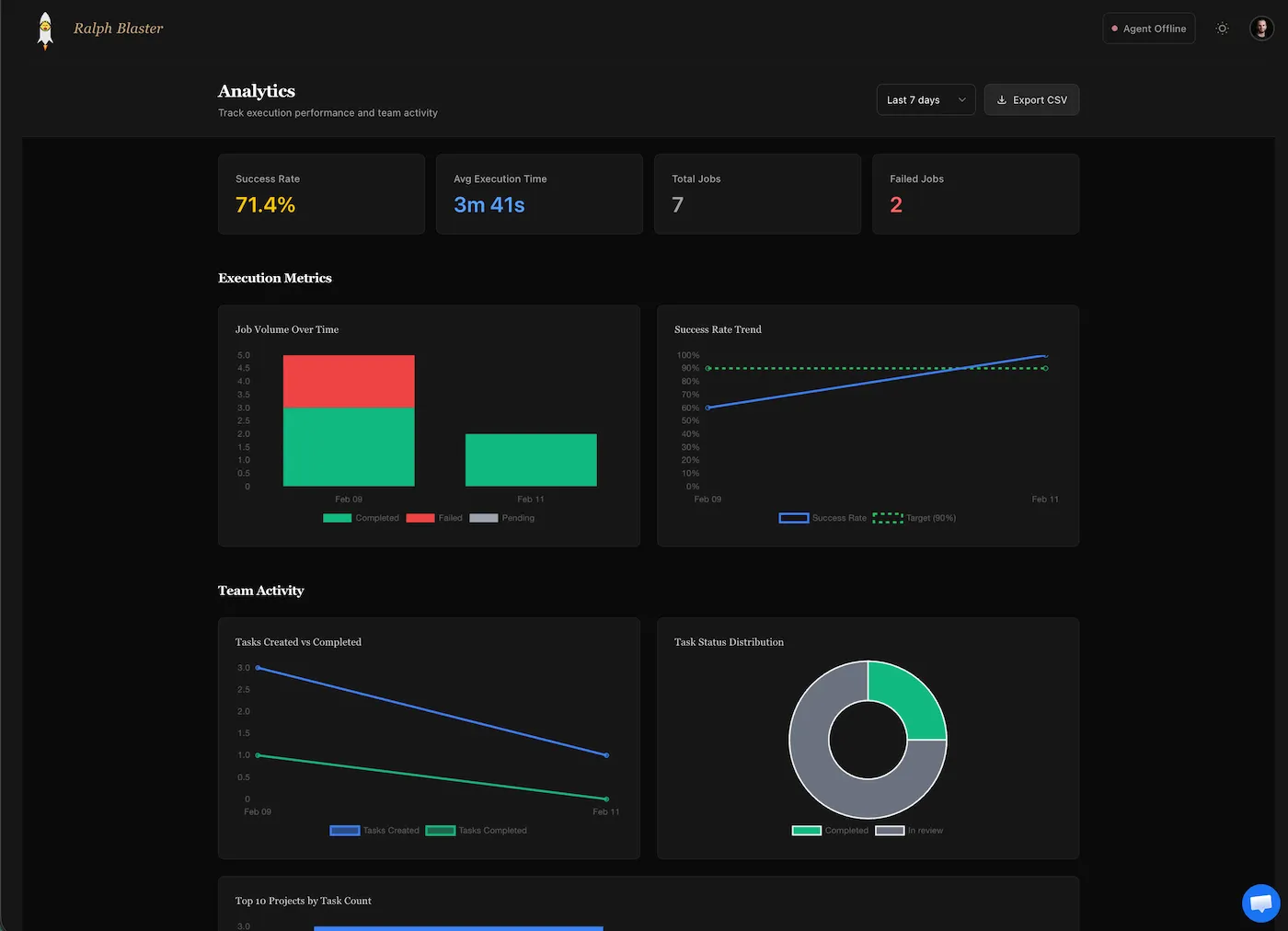
Track speed and reliability with analytics
RalphBlaster includes a built-in analytics view for throughput and quality monitoring. The example shown reports a 71.4% success rate, 3m 41s average execution time, and visibility into failed jobs and task status distribution.
| Metric | Example Value (Screenshot) | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Success Rate | 71.4% | Signals output quality and process stability. |
| Average Execution Time | 3m 41s | Tracks operational speed per task run. |
| Total Jobs / Failed Jobs | 7 / 2 | Quantifies reliability and iteration load. |
Who this workflow is for (and not for)
| Best Fit | Not a Great Fit |
|---|---|
| Small SaaS teams that need faster feature throughput with clear review checkpoints. | Teams expecting fully hands-off production deploys with zero human QA. |
| Founders and product engineers who already work from tickets and PR workflows. | Projects with no issue tracking, no branching discipline, or no code review habit. |
| Roadmaps with repeatable enhancement patterns that benefit from templates. | Highly novel R&D tasks where requirements are too fluid for template-driven execution. |
What it costs to run this AI SaaS development workflow
Cost is a stack, not a single line item. The onboarding flow also notes that Claude Code billing is separate from the RalphBlaster subscription and references a typical usage recommendation around the Claude side.
| Cost Component | How to Think About It |
|---|---|
| RalphBlaster subscription | Platform fee for workflow orchestration, ticket execution, and team visibility. |
| Claude Code usage | Model billing is separate. Track spend per task class to avoid silent cost creep. |
| Validation overhead | Tests, QA, and review time are still required and should be budgeted explicitly. |
| Iteration/failure budget | Some runs will fail or require regeneration. Plan for retries in both time and spend. |
Limitations and tradeoffs to expect
- A faster loop can still produce weak output if ticket scope and acceptance criteria are vague.
- Autonomous execution reduces keyboard time but increases the need for disciplined review gates.
- Template quality becomes a leverage point; poor templates amplify poor outcomes.
- Failure rate matters: optimizing for speed alone can hide expensive retry and rework patterns.
- This workflow improves throughput, but it does not replace architecture decisions or product judgment.
Quality guardrails that prevent AI speed from becoming tech debt
- Keep implementation isolated in branches/worktrees before merge.
- Use PRD or analysis templates for higher-risk work to reduce ambiguity.
- Require human code review and local validation before shipping.
- Track failures in analytics and tighten templates where runs break.
Internal links to weave into final copy: SaaS Growth Strategy, SaaS Growth Audit, How to Buy a SaaS Business, Startup Resources, and Wildfront Community.
FAQ: AI SaaS development
What is AI SaaS development?
AI SaaS development is a repeatable delivery system where tickets, planning templates, autonomous coding runs, and human review gates combine to ship software faster without giving up quality control.
How much faster can AI agents build SaaS features?
Speed gains depend on your baseline, but the right way to report them is with measurable values like lead time, average execution duration, and failure rate, not generic \"10x\" claims.
Is autonomous AI coding safe for production apps?
It can be, when runs are isolated, code is reviewed before merge, and teams enforce validation checks before release.
Should I use Claude Code for SaaS work?
If your current workflow is Claude-first, use Claude consistently and optimize the surrounding process. Standardized templates, isolated execution, and strict review gates drive most of the speed gains.
What is the difference between AI in SaaS and an AI SaaS platform?
AI in SaaS usually refers to product features for end-users. An AI SaaS platform can also describe the internal delivery system teams use to build and ship those features faster.
Final takeaway
The strongest angle for ranking and conversion is simple: show the full workflow with evidence. RalphBlaster's ticket, template, execution, Kanban, and analytics views make the \"build SaaS faster with AI\" claim concrete and auditable.
Try the workflow in your own SaaS stack
See how RalphBlaster can run coding tasks autonomously while your team controls standards, reviews, and release quality.
